
Buy Diazepam 10mg 30 tablets
$96.52
Diazepam 10 mg tablets are potent benzodiazepine derivatives used in research settings, characterized by a pale yellow crystalline form and a well-understood profile in GABA modulation.
Important Notice:
European customers should complete their purchases in USD (not CAD). After placing your order and before manual payment, the currency will be converted to Euros.
Canadian customers should use CAD, and American customers should use USD.
Diazepam 10mg 30 Tablets Product Description
Introduction
Diazepam is a synthetic chemical compound that belongs to the benzodiazepine class. It is most commonly supplied as tablets of various strengths, including 10 mg, and is used extensively in research and clinical settings. Diazepam tablets appear as small, pale yellow to white crystalline solids, designed for oral administration. The compound is well-known for its distinct chemical structure, which features a fused benzodiazepine ring system. Diazepam is a solid form chemical, stable under standard storage conditions, and widely utilized in pharmaceutical and biochemical research labs.
Chemical Properties and Specifications
Structural and Molecular Characteristics
-
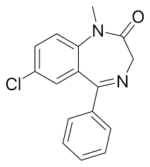
Chemical Formula: C16H13ClN2O
-
Molecular Weight: 284.74 g/mol
-
CAS Number: 439-14-5
-
IUPAC Name: 7-chloro-1-methyl-5-phenyl-1,3-dihydro-2H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
-
Synonyms: Diazepam, Methyl diazepinone, RO 5-2807, Valium (brand name)
Physical Properties and Purity Standards
-
Appearance: Colorless to pale yellow crystalline powder
-
Purity: ≥99% standard for research-grade material
-
Solubility: Practically insoluble in water, soluble in alcohol, chloroform, ether
-
Storage Recommendations: Store in a cool, dry place away from light and moisture, typically at room temperature (15-25°C)
Pharmacological Profile and Mechanism of Action
Proposed Mechanism of Action
Diazepam acts primarily through modulating gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) neurotransmission. It enhances the effect of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA by binding to the benzodiazepine site on the GABA-A receptor complex. This binding facilitates increased chloride ion influx, hyperpolarizing neuronal membranes and leading to central nervous system depression, which accounts for its sedative and anxiolytic effects.
Research Applications
Diazepam is widely used in neuropharmacological research to study GABAergic pathways, receptor binding, and central nervous system depressants. It serves as a standard compound in experiments involving anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, muscle relaxant, and sedative models. Additionally, diazepam is utilized in analytical chemistry for assay development, pharmacokinetics, and metabolism studies.
Comparative Analysis with Related Compounds
Compare to Related Compounds
Diazepam is often compared to other benzodiazepines such as lorazepam, clonazepam, and alprazolam. Compared to these, diazepam has a longer half-life and produces active metabolites, leading to prolonged effects. Its lipophilicity is moderate, balancing central nervous system penetration and systemic distribution.
Advantages for Research
The long half-life and well-characterized metabolism of diazepam enable extended observation periods in experimental models. Its availability in a stable oral tablet form (such as 10mg tablets) simplifies dosing in animal and in vitro studies. Diazepam’s broad acceptance in clinical research and extensive pharmacological data facilitate comparative and translational research objectives.
Safety and Handling Guidelines
Laboratory Safety
Handle diazepam with appropriate personal protective equipment including gloves and eye protection. Avoid inhalation of dust or powders. Use in well-ventilated fume hoods when handling powder forms to minimize exposure.
Disposal and Environmental Considerations
Dispose of diazepam in accordance with institutional hazardous waste guidelines. Prevent release into the environment by following chemical waste regulations and avoid flushing unused material into water systems.
Regulatory Status
Diazepam is a controlled substance in many countries due to its pharmacological effects. It is strictly regulated and should only be used for research purposes where permitted by law. Researchers must comply with all regulatory requirements for storage, handling, and documentation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What is the molecular formula of diazepam?
The molecular formula is C16H13ClN2O. -
Is diazepam soluble in water?
Diazepam is practically insoluble in water but soluble in solvents like alcohol and chloroform. -
What class of compounds does diazepam belong to?
Diazepam is classified as a benzodiazepine. -
What is the primary mechanism of action of diazepam?
It enhances the inhibitory action of GABA in the central nervous system by binding to GABA-A receptors. -
How should diazepam tablets be stored?
Store at controlled room temperature in a dry, light-protected environment.
Conclusion
Diazepam 10 mg tablets represent a well-known and widely studied benzodiazepine compound with well-defined chemical, physical, and pharmacological characteristics. Its role in research mainly focuses on GABAergic neurotransmission and central nervous system modulation. The compound’s stability, established safety protocols, and regulatory framework make it a staple in experimental and analytical research involving sedative and anxiolytic agents.
Related products

Buy Ativan 1MG
$4,852.10 – $26,226.73Price range: $4,852.10 through $26,226.73
Buy Clonazolam Pellets 1mg
$7,867.60 – $28,849.26Price range: $7,867.60 through $28,849.26
Buy Fluclotizolam 0.5mg Pellets
$206.82 – $1,365.04Price range: $206.82 through $1,365.04
Buy Methaqualone (Quaalude) 300mg
$1,116.85 – $65,550.96Price range: $1,116.85 through $65,550.96
Buy Suboxone 2mg
$412.27 – $894.86Price range: $412.27 through $894.86












Reviews
There are no reviews yet.